Lumacaftor
Le lumacaftor (code du médicament VX-809) est un médicament expérimental pour traiter les patients atteints de mucoviscidose, développé par Vertex Pharmaceuticals. Ce médicament est développé pour les patients présentant la mutation F508del homozygote de la protéine CFTR, cause de la maladie. Cela représente environ 60 % des patients atteints de mucoviscidose et près de 90 % des mutations de la protéine CFTR. Le combiné Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor a reçu aux États-Unis en et obtenu en en France une autorisation temporaire d'utilisation (ATU), sous le nom commercial de Orkambi.
| Lumacaftor | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
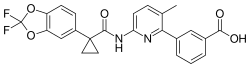
| Nom UICPA | acide 3-{6-{[1-(2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)cyclopropanecarbonyl]amino}-3-méthylpyridin-2-yl}benzoïque |
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.241.800 |
| PubChem | 16678941 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Apparence | comprimé |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C24H18F2N2O5 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 452,406 9 ± 0,022 4 g/mol C 63,72 %, H 4,01 %, F 8,4 %, N 6,19 %, O 17,68 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier |
|
Mode d'action
modifierLe lumacaftor permet d'augmenter la fonction de la protéine CFTR déficiente, conduisant en une amélioration de la sécrétion de l'ion chlore[2].
Efficacité
modifierUtilisé seul, son efficacité n'est pas démontré[3]. En association avec l'ivacaftor, il permet, chez les patients présentant la mutation F508del homozygote, d'améliorer les résultats de la spirométrie et de diminuer le nombre d'exacerbations de la maladie[4].
Il pourrait traiter certains types de syndrome du QT long[5].
Notes et références
modifier- ↑ Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- ↑ Van Goor F, Hadida S, Grootenhuis PD et al. Correction of the F508del-CFTR protein processing defect in vitro by the investigational drug VX-809, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011;108:18843-18848
- ↑ Clancy JP, Rowe SM, Accurso FJ et al. Results of a phase IIa study of VX-809, an investigational CFTR corrector compound, in subjects with cystic fibrosis homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation, Thorax, 2012;67:12-18
- ↑ Wainwright CE, Elborn JS, Ramsey BW et al. Lumacaftor–Ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis homozygous for Phe508del CFTR, N Engl J Med, 2015;373:220-231
- ↑ Mehta A, Ramachandra CJA, Singh P et al. Identification of a targeted and testable antiarrhythmic therapy for long-QT syndrome type 2 using a patient-specific cellular model, Eur Heart J, 2018;39:1446–1455