CDK4
gène de l'espèce Homo sapiens
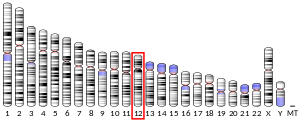
La CDK4 est une kinase dépendante des cyclines. Son gène est le CDK4 situé sur le chromosome 12 humain.
Fonction de Cdk4
modifierLe complexe Cdk4-cycline D phosphoryle la pRB, engendrant un changement conformationnel la rendant inactif, libérant E2F et permettant à la cellule de progresser dans le cycle cellulaire.
En médecine
modifierCette protéine joue un rôle dans la prolifération cellulaire, notamment dans les cancers[4], constituant une cible thérapeutique. Le palbociclib[5] et le ribociclib[6] sont des inhibiteurs des CDK4 et CDK6 efficaces dans certains cancers du sein.
Notes et références
modifier- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000135446 - Ensembl, May 2017
- « Publications PubMed pour l'Homme », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- « Publications PubMed pour la Souris », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Hamilton E, Infante JR, Targeting CDK4/6 in patients with cancer, Cancer Treat Rev, 2016;45:129-138
- Finn RS, Crown JP, Lang I et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): a randomised phase 2 study, Lancet Oncol, 2015;16:25-35
- Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA et al. Ribociclib as first-line therapy for HR-positive, advanced breast cancer, N Engl J Med, 2016;375:1738-1748