2014 FE72
objet transneptunien
2014 FE72 est un objet transneptunien détaché. Son orbite est très allongée, il s'approche à proximité de l'orbite de Neptune et s'éloigne jusqu'à une distance environ cent fois plus importante. Il a été découvert en 2014, mais sa découverte a été annoncée le .
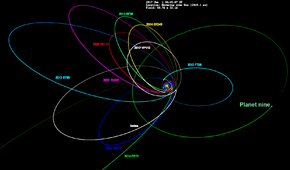
Orbite de 2014 FE72 en vert pâle, orbites d'autres corps et de l'hypothétique Planète Neuf en vert à droite.
| Demi-grand axe (a) |
196,72 × 109 km (1 315 ± 412 ua) |
|---|---|
| Périhélie (q) |
5,414 × 109 km (36,19 ± 0,14 ua) |
| Aphélie (Q) |
388,05 × 109 km (2 594 ± 813 ua) |
| Excentricité (e) | 0,972 |
| Période de révolution (Prév) |
17 420 485 j (47694 ± 9000 a) |
| Inclinaison (i) | 20,69° |
| Longitude du nœud ascendant (Ω) | 336,76° |
| Argument du périhélie (ω) | 133,7° |
| Anomalie moyenne (M0) | 0,418° |
| Catégorie | Objet détaché |
| Dimensions | 265 km[3] |
|---|---|
| Magnitude absolue (H) | 6,1 |
| Date | |
|---|---|
| Découvert par |
Scott S. Sheppard Chadwick Trujillo |
| Lieu | Cerro Tololo |
| Désignation | 2014 FE72 |
Annexes
modifierArticles connexes
modifierRéférences
modifier- (en) Caractéristiques et simulation d'orbite de 2014FE72 dans la JPL Small-Body Database.
- (en) Minor Planet Center database
- (en) « Liste des objets transneptuniens », sur Johnston's Archive